Biogas Plants: Transforming Waste into Energy
Introduction
In the era of climate change and energy crises, biogas plants have emerged as a revolutionary solution — converting organic waste into clean, renewable energy. With their dual benefits of waste management and energy production, biogas plants are reshaping how we view sustainable living.
Let’s dive deep into the science behind biogas plants, explore real-world case studies, and understand how they can drive a greener future.
What is a Biogas Plant?
A biogas plant is a system that processes organic waste — such as animal manure, food scraps, and crop residues — through anaerobic digestion. This biological process produces:
- Biogas: A mixture of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), used as fuel for cooking, electricity generation, and heating.
- Digestate: A nutrient-rich residue used as an organic fertilizer.
Working of a Biogas Plant
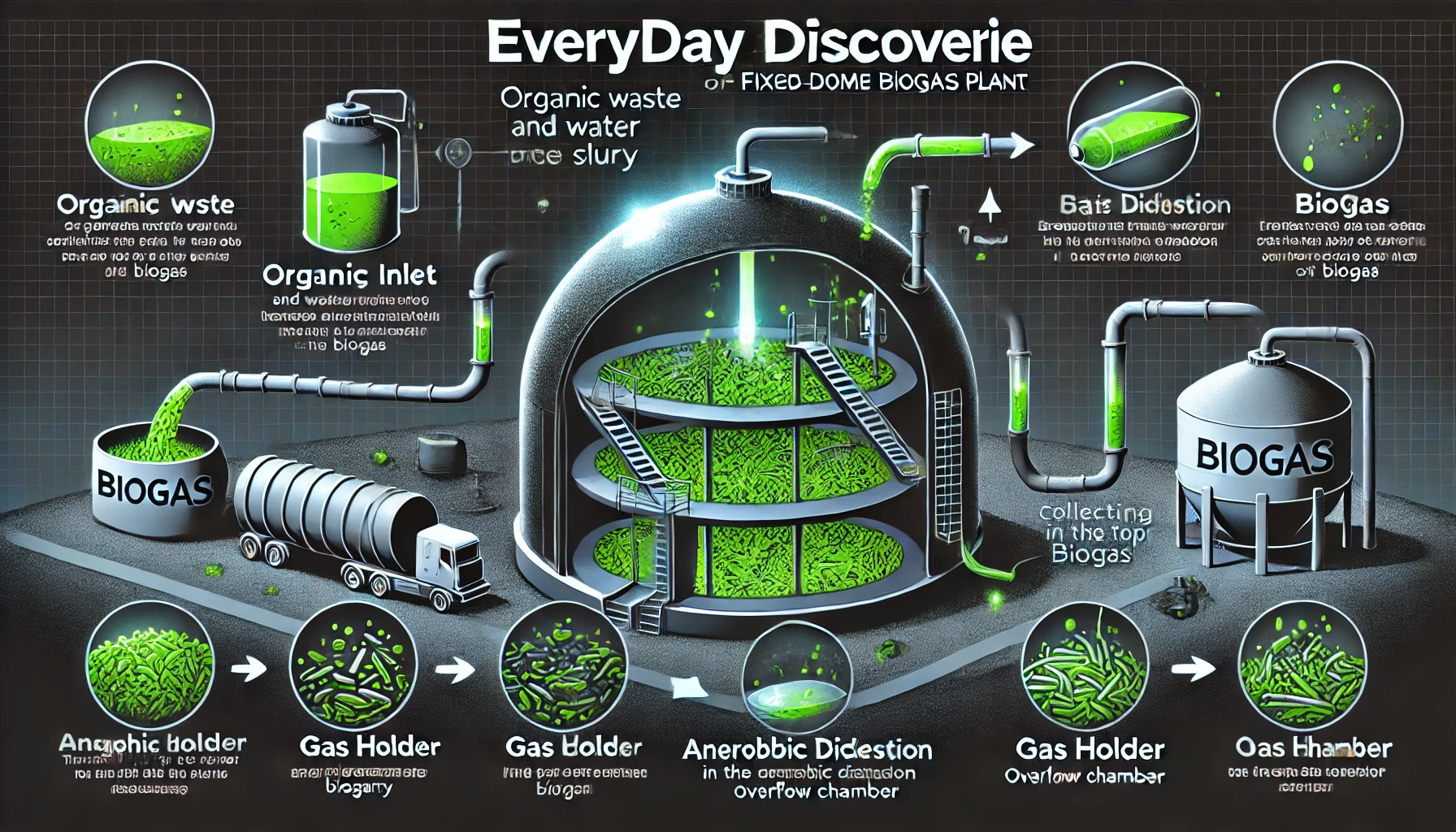
Let’s break down the functioning of a typical biogas plant:
Step-by-Step Process:
-
Feedstock Collection:
- Organic waste (cow dung, food scraps, agricultural residue) is gathered.
- Water may be added to form a slurry for easy digestion.
-
Input into Digester:
- The slurry is fed into the anaerobic digester — an airtight tank.
-
Anaerobic Digestion:
- Bacteria break down organic matter through four key stages:
- Hydrolysis: Complex organic matter breaks into simple molecules.
- Acidogenesis: Simple molecules turn into organic acids and alcohols.
- Acetogenesis: Acids are converted into acetic acid, CO2, and hydrogen.
- Methanogenesis: Methane bacteria convert acetic acid and gases into biogas (CH4 + CO2).
-
Gas Collection:
- Biogas rises and is collected in a gas holder.
-
Biogas Usage:
- Used for cooking, heating, electricity generation, and vehicle fuel (after purification).
-
Digestate Extraction:
- The leftover slurry is removed and used as organic fertilizer.
Types of Biogas Plants
1. Fixed Dome Biogas Plant:
- Structure: A digester with a fixed, immovable gas holder.
- Process: As biogas accumulates, it displaces the slurry into an overflow chamber.
- Advantages: Low-cost, durable, and suitable for rural areas.
- Disadvantages: Gas pressure fluctuates, which can make usage inconsistent.
2. Floating Drum Biogas Plant:
- Structure: A movable gas holder floats above the digester.
- Process: The drum rises and falls with gas production.
- Advantages: Easier to monitor gas levels and output.
- Disadvantages: Higher maintenance and risk of corrosion.
3. Balloon Biogas Plant:
- Structure: A flexible digester and gas holder combined in an inflatable bag.
- Process: Suitable for small-scale or temporary setups.
- Advantages: Portable and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: Less durable compared to dome or drum plants.
Technical Diagram of a Fixed Dome Biogas Plant
Here’s a clear illustration of how a fixed dome biogas plant works:
+----------------------------+
| Gas Holder | ← Collects biogas (CH4 + CO2)
+----------------------------+
| Digester Tank | ← Organic waste decomposes
| (Anaerobic Chamber) |
+----------------------------+
| Slurry Inlet | ← Feedstock (dung + water)
+----------------------------+
| Overflow Chamber | ← Excess slurry exits
+----------------------------+
Real-Life Case Studies of Biogas Plants
1. Biogas Plant in Pune, India
- Location: A municipal biogas plant processes 10 tons of organic waste daily.
- Outcome: Produces 1000 m³ of biogas per day, powering streetlights and public kitchens.
- Impact: Reduced landfill waste by 30%, saving Ōé╣20 lakhs annually.
2. Gobar-Dhan Scheme, Haryana
- Objective: Convert cattle dung into biogas and organic manure.
- Result: Over 200 rural biogas plants set up, cutting down firewood use and promoting clean cooking fuel.
3. Community Biogas Plant, Bihar
- Model: Combines agricultural residue and cow dung to produce biogas for 50 households.
- Success: Replaced 60% of LPG usage, with surplus gas sold to nearby villages.
Advantages of Biogas Plants
1. Renewable Energy Source:
Biogas is a clean and renewable energy alternative, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
2. Waste Management:
Efficiently disposes of organic waste, cutting down landfill overflow and methane emissions.
3. Climate Change Mitigation:
Captures methane — a greenhouse gas 25x more potent than CO2 — preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere.
4. Energy Independence:
Provides rural households with free, sustainable fuel for cooking and heating.
5. Organic Fertilizer Production:
Digestate is a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer, improving soil health and crop productivity.
Challenges of Biogas Plants
- High Initial Cost: Setting up plants requires significant investment.
- Technical Expertise: Proper design, operation, and maintenance need trained personnel.
- Feedstock Availability: Consistent supply of organic waste is essential.
- Public Awareness: Lack of knowledge hinders rural adoption.
Government Initiatives in India
1. SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation):
- Launched in 2018 to promote compressed biogas (CBG) plants.
- Aims to set up 5,000 CBG plants by 2030.
2. Gobar-Dhan Yojana:
- Converts cattle dung and organic waste into biogas and manure.
- Empowers rural communities by promoting waste-to-wealth concepts.
3. National Biogas and Manure Management Programme (NBMMP):
- Offers subsidies for family-type biogas plants.
- Focuses on rural energy security and organic farming.
Conclusion
Biogas plants are more than just an energy solution — they are a catalyst for sustainable development. From reducing waste and curbing greenhouse gas emissions to providing clean cooking fuel and organic fertilizers, these plants are the cornerstone of green energy transitions.
As India aims for net-zero emissions by 2070, biogas technology will play a vital role in bridging the gap between energy demand and environmental conservation.
Let’s invest in biogas solutions, educate communities, and build a future where waste fuels progress.